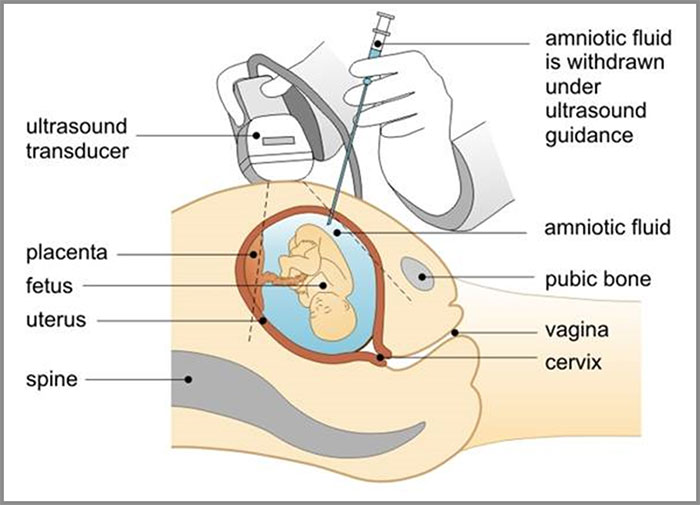
Amniocentesis is a procedure in which amniotic fluid is removed from the uterus for testing or treatment. Amniotic fluid is the fluid that surrounds and protects a baby during pregnancy. This fluid contains fetal cells and various proteins.
Why it's done
Amniocentesis can be done for various reasons:
• Genetic testing. Genetic amniocentesis involves taking a sample of amniotic fluid and testing it for certain conditions, such as Down syndrome.
• Diagnosis of fetal infection. Occasionally, amniocentesis is used to evaluate a baby for infection or other illness.
• Treatment. If you accumulate too much amniotic fluid during pregnancy (polyhydramnios), amniocentesis might be done to drain excess amniotic fluid from your uterus.
Genetic amniocentesis
Genetic amniocentesis is usually done between weeks 15 and 20 of pregnancy. Amniocentesis done before week 15 of pregnancy has been associated with a higher rate of complications.
You might consider genetic amniocentesis if:
• You had positive results from a prenatal screening test.
• You had a chromosomal condition in a previous pregnancy.
• You have a family history of a specific genetic condition, or you or your partner is a known carrier of a genetic condition.
• You have abnormal ultrasound findings.
Source: Mayo Clinic